THM - Advent of Cyber 2022 - Day 13¶

Difficulty:
Challenge Link
OS: Linux
After receiving the phishing email on Day 6 and investigating malware on Day 12, it seemed everything was ready to go back to normal. However, monitoring systems started to show suspicious traffic patterns just before closing the case. Now Santa's SOC team needs help in analysing these suspicious network patterns.
Learning Objectives¶
- Learn what traffic analysis is and why it still matters.
- Learn the fundamentals of traffic analysis.
- Learn the essential Wireshark features used in case investigation.
- Learn how to assess the patterns and identify anomalies on the network.
- Learn to use additional tools to identify malicious addresses and conduct further analysis.
- Help the Elf team investigate suspicious traffic patterns.
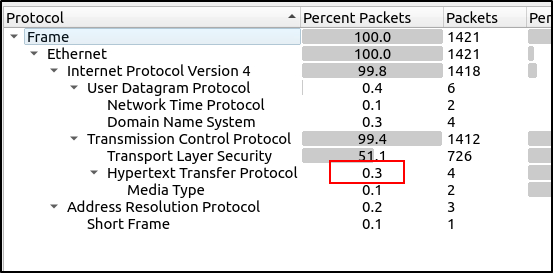
What is the "Percent Packets" value of the "Hypertext Transfer Protocol"?
Which port number has received more than 1000 packets?
What is the service name of the used protocol that received more than 1000 packets?
Common Port Name
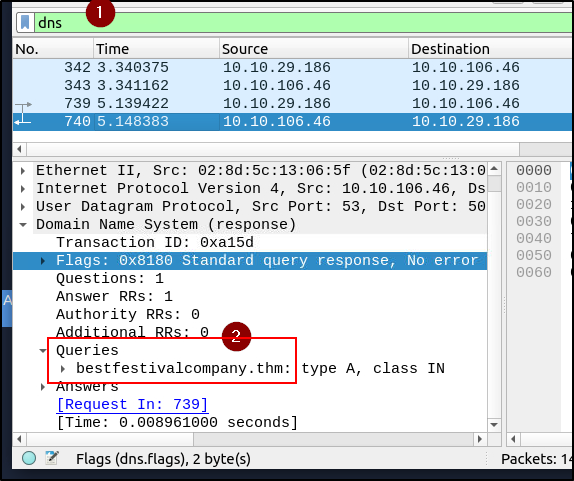
What are the domain names?
Filter the DNS packets.
Enter the domains in alphabetical order and defanged format. (format: domain[.]zzz,domain[.]zzz)
We can use dns in the wireshark search field to filter by dns packets.
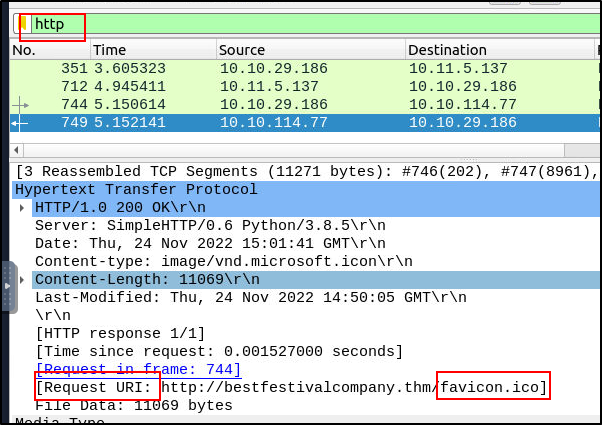
What are the names of the requested files?
Filter the HTTP packets.
Enter the names in alphabetical order and in defanged format. (format: file[.]xyz,file[.]xyz)
Similar to the previous one we can filter by HTTP and then look in the HTTP Section of the Packet.
Which IP address downloaded the executable file?
Enter your answer in defanged format.
Looking back on the same filter as above at the .exe packet you can see the source IP.
Which domain address hosts the malicious file?
Enter your answer in defanged format.
Looking at the same packet. We can see the source url of that file from where it was downloaded.
What is the "user-agent" value used to download the non-executable file?
Let's look back at the other packet and check the user-agent field.

What is the sha256 hash value of the executable file?
Export objects from the PCAP file.
Calculate the file hashes.
We can export the HTTP Objects and select the .exe from the list. Then run sha256sum against it.

Search the hash value of the executable file on VirusTotal.
Navigate to the "Behaviour" section.
There are multiple IP addresses associated with this file.
What are the connected IP addresses?
Enter the IP addressed defanged and in numerical order. (format: IPADDR,IPADDR)
Please note that the VT entry changed since the official walkthrough video was recorded - check the VT website to get all the IP addresses you need!